

Sketch the molecular shape of the compounds in the table below. Which of these three previous molecules will have all bond angles equal to each other? Explain completely.Ĥ.

Subsequent replacements of H with Cl yield dichloromethane (CH2Cl2), trichlormethane (CHCl3) and tetrachlormethane (CCl4).
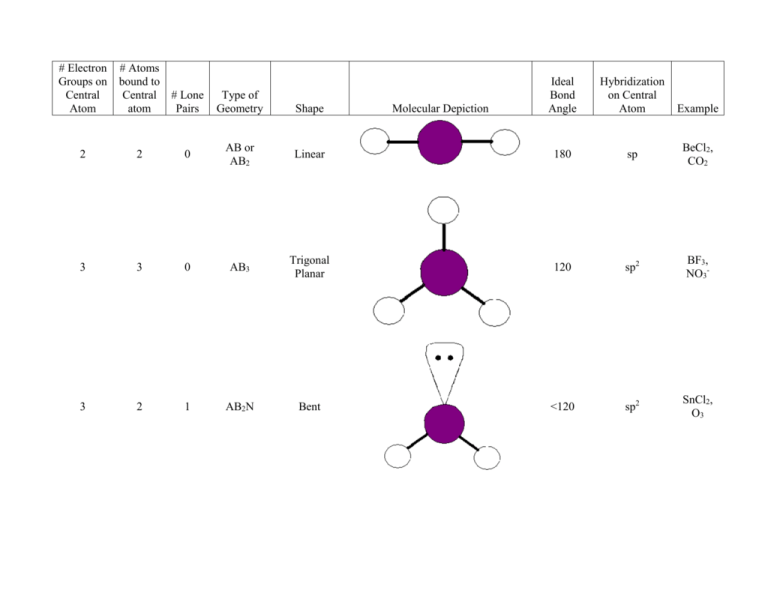
Chloromethane can be thought of as resulting from methane via the replacement of one Hydrogen atom with a Chlorine atom. What is the molecular geometry (shape) of the chloromethane molecule (CH3Cl)? Explain completely why NOT all of the bond angles in chloromethane are equal.ģ. What is the molecular geometry (shape) of the methane molecule (CH4)? Explain completely why all the bond angles in methane are equal.Ģ. Part 2: Construct the three-dimensional geometry for the molecules listed in Table 2.ġ. Part 1: Use your Periodic Table of Elements to determine the elemental symbol, group number and valence electrons for the elements listed in Table 1. In this experiment, you will predict the three-dimensional geometry of a series of neutral molecules using the VSEPR theory.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
